Multiple cloud data centers are already on the horizon and they are signaling a brand-new era of cloud computing that is virtually quite dynamic, scalable and immensely cost effective. With the help of given cloud platforms, the enterprises can adjust the infrastructure of IT to meet peculiar business needs, thus improving the ability and protection at the same level. By having multiple clouds, it eradicates the risks associated with a single vendor and also fosters new opportunities for development.
Let’s dive deep into the RISE…
- Risk Mitigation and Business Continuity:
Services deployed across multiple providers help lessen the impact of failures since they can be quickly moved, or load balanced among multiple providers. If a certain provider is in difficulty, services can easily switch over to the other service provider to avoid interruptions and develop strong solutions for disasters.
- Cost Optimization:
With multi-cloud, there is a possibility of optimizing on the pricing differences across the different cloud services. Interference with the workloads following the cost and performance parameters may help to regulate the cloud expenses and simultaneously, it helps to prevent the vendor lock-in.
- Geographical Expansion:
The enterprises should be able to have multiple cloud data centers to serve different regions to meet the data sovereignty and get close to the users in different areas for better experience and compliance with regional laws.
- Hybrid Development:
Multi cloud may therefore be used by cloud organizations to easily connect on premise infrastructures to public cloud services. Cloud approach helps enterprises to regain business continuity for multi cloud architectures by offering a reliable disaster recovery solution capable of mirroring data applications across the multiple cloud services. For this reason, in the case of the service outage occurrence, organizations are free to switch to another provider of cloud services in order to ensure business preservation and minimize the losses. One way is an ability to increase the result of organizations by choosing among cloud providers and selecting the most appropriate cloud service for some types of workloads, for instance, using the one provider for high speed while using the other one for enhanced capability to store.
- Vendor Diversification:
Divesting discretion from one cloud provider decreases vulnerability to vendor problems, new expensive charges, and restricted service. This way the organizations can gain flexibility and bargaining power of negotiations with the multiple providers.
- Regulatory Compliance:
The complexity of meeting regulation rules different concerning the residency and sovereignty of data is also solved by an organization using multi-cloud environments. Spreading data across more than one cloud host guarantees compliance to the law like GDPR, HIPAA as well as PCI-DSS.
Implementations of Multi-Cloud Data Centers
- Enhanced Data Security:
Multi-cloud strategies enhance strong data security by dispersing data across multiple platforms, reducing the impact of cyber-attacks and minimizing the risk of breaches.
- E-commerce Optimization:
E-commerce companies can leverage multi cloud capabilities to handle high volumes of traffic efficiency, ensuring seamless customer experiences and robust transaction processing.
- Global Enterprise Utilization:
Enterprises utilize multi-cloud strategies to adhere to local data laws and access region-specific services, enhancing operational efficiency and compliance.
Future of Multi-Cloud Data Centers
The future of multi-cloud data centers is promising, with emerging technologies like AI and machine learning set to streamline the cloud management. Moreover, the integration of edge computing is expected to boost data processing capabilities and performance. This evolution will enhance better communication and coordination among the distributed development teams, accelerating innovation and delivering better products to market.
“Gartner’s cloud shift research includes only those enterprise IT categories that can transition to cloud, within the application software, infrastructure software, business process services and system infrastructure markets. By 2025, 51% of IT spending in these four categories will have shifted from traditional solutions to the public cloud, compared to 41% in 2022. Almost two-thirds (65.9%) of spending on application software will be directed toward cloud technologies in 2025, up from 57.7% in 2022.”
Source: Gartner
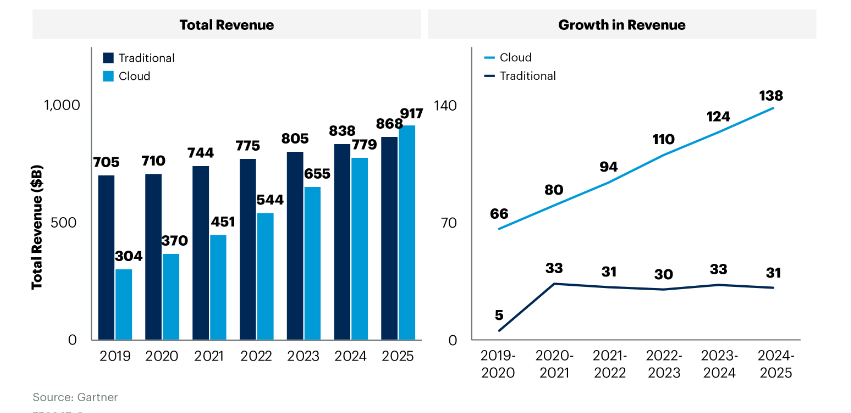
Gartner says more than half of enterprise IT spending in key market segments will shift to the cloud by 2025
- Multi Cloud: The Future of Cloud Computing
Multi-cloud is emerging as a significant trend and potential direction for the cloud computing industry. This approach involves using multiple cloud service providers to fulfill diverse business requirements, reducing the dependence on a single provider.
- Accessing Data from Various Cloud Providers
Starburst simplifies the integration of multiple cloud providers by offering a unified data access interface that eliminates the complexities of individual platform APIs, enabling users to focus on data exploration and analysis.

Major Cloud Computing Utilizations
- Data Storage and Backup
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Big Data Analytics
- Development and Testing Environments
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
- Online Data Storage:
Cloud computing enables manage and access of files and images, music, and movies, which are convenient, fast, and elastic storage services. These platforms offer vast security means such as encryption and the use of a multi-factor authenticator which prevent the information from unauthorized access.
- Backup and Recovery:
Cloud service providers provide secure back up services meant to support management in case there is an occurrence of a disaster; these services support faster restoration of normalcy with minimal loss. CDR or Cloud DR is the plan incorporated in the services and methods regarding the protection of the data, applications, and assets. This protection is accomplished by changing the aspects that exist in the public cloud environments to the dedicated services provider.
- Big Data Analysis:
Cloud platforms offer affordable high-performance computing solutions for handling big data to support new solutions and business development in sectors including the healthcare sector, the finance sector and retail, manufacturing and telecommunications sectors.
- Testing and Development:
The cloud computing thus provides a flexible but scalable infrastructure for development and testing thus cutting down the time to market while at the same time increasing the overall quality of the product. The flexibility of pay-as-you-go model enables the businesses to contain the cost, which leads to improved cooperation of the dispersed development teams.
Conclusion: Embracing the Multi-Cloud Future
In the current world that is characterized by constant competition and fast-changing environments that organizations operate, multi-cloud data centers are a solution that best fits the due environment since they improve the adaptability, scalability and costs. This way, utilizing several cloud platforms, business can reduce the exposure to threats, enhance the cost efficiency, and satisfy the legal requirements while increasing the geographical presence. It is suggested that multi-cloud data centers are yet to become more innovative and operationally superior through incorporation of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and edge computing. Moving to a multi-cloud approach is not just about being relevant—It’s about being relevant tomorrow and the day after tomorrow and the day after that in a world that’s becoming increasingly digital.
Ready to transform your IT infrastructure and getting the most out of multi-cloud data centers? Find out how Sensiple can assist your organization in levelling up multi-cloud solutions for innovation, performance, and business resilience.
Author:

Hemanth Kumar Siamsundar, Junior Developer at Sensiple, brings 4.7 years of specialized experience in IVR solutions. Has a strong command of JavaScript and Node.js, and has effectively handled various projects involving Comcast, Twilio, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), Contact Center Services, and West utilities.







